FoodMyths, NutritionScience, DietaryMyths, HealthyEating, NutritionalFacts, DebunkingMyths, BalancedDiet, NutritionFacts, EatingHabits, EvidenceBasedNutrition
In the ever-evolving landscape of nutrition science, myths and misconceptions about food abound. From trendy fad diets to age-old beliefs passed down through generations, separating fact from fiction can be a daunting task. In this blog, we'll debunk some of the most common food myths and explore the scientific evidence behind them.
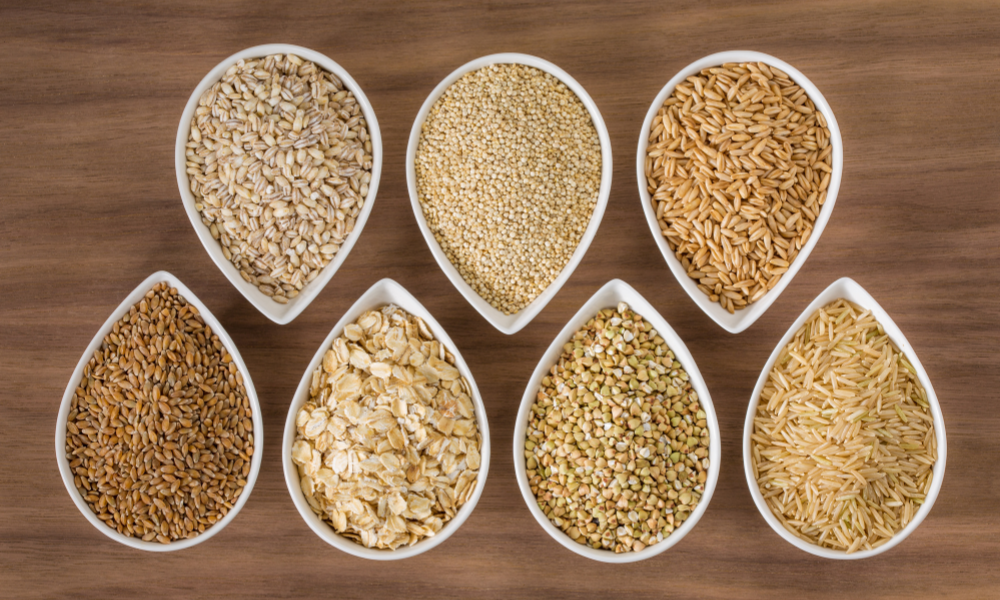
Myth 1: Carbs are the Enemy One of the most pervasive myths in nutrition is the vilification of carbohydrates. While it's true that refined carbohydrates like white bread and sugary snacks should be consumed in moderation, not all carbs are created equal. Complex carbohydrates found in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables are essential sources of energy and provide valuable nutrients like fiber, vitamins, and minerals. The key is to focus on quality carbs and balance them with protein and healthy fats for optimal health.
Myth 2: Eating Fat Makes You Fat Contrary to popular belief, eating fat does not necessarily lead to weight gain. In fact, healthy fats like those found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil are an essential part of a balanced diet and can actually promote satiety and weight loss when consumed in moderation. The key is to choose unsaturated fats over saturated and trans fats and limit intake of processed and fried foods.
Myth 3: Egg Yolks are Unhealthy For years, egg yolks have been demonized for their cholesterol content. However, research has shown that dietary cholesterol has little impact on blood cholesterol levels for most people. Eggs are a nutrient-rich food packed with protein, vitamins, and minerals, and the yolks contain important nutrients like choline and lutein that support brain and eye health. Unless you have specific dietary restrictions, there's no need to fear the humble egg yolk.
Myth 4: Eating Late at Night Causes Weight Gain The notion that eating after a certain time of day will automatically lead to weight gain is a persistent myth with little scientific basis. Weight gain is determined by the total number of calories consumed versus calories burned, regardless of the time of day. While it's true that late-night snacking can lead to overeating and poor food choices, what matters most is the quality and quantity of food consumed throughout the day rather than the timing.
Myth 5: Organic Food is Always Healthier While organic food is grown without synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, it's not necessarily healthier or more nutritious than conventionally grown produce. Studies have shown mixed results when comparing the nutritional content of organic and conventional foods, and factors like soil quality, farming practices, and ripeness at harvest can all influence nutrient levels. Organic farming practices may have environmental benefits, but choosing organic is a personal decision and not a guarantee of superior nutritional quality.
In the world of nutrition science, separating fact from fiction can be challenging amidst the abundance of myths and misconceptions surrounding food. By critically evaluating the scientific evidence and consulting reputable sources, we can debunk common food myths and make informed choices about our diets. Remember, there's no one-size-fits-all approach to nutrition, and a balanced diet rich in whole foods is the foundation of good health.
Powered by: Oh! Puhleeez Branding Agency & NowUpskill
FoodMyths, NutritionScience, DietaryMyths, HealthyEating, NutritionalFacts, DebunkingMyths, BalancedDiet, NutritionFacts, EatingHabits, EvidenceBasedNutrition