Electric Vehicles, Electric Engines, Sustainable Transportation, Automotive Technology
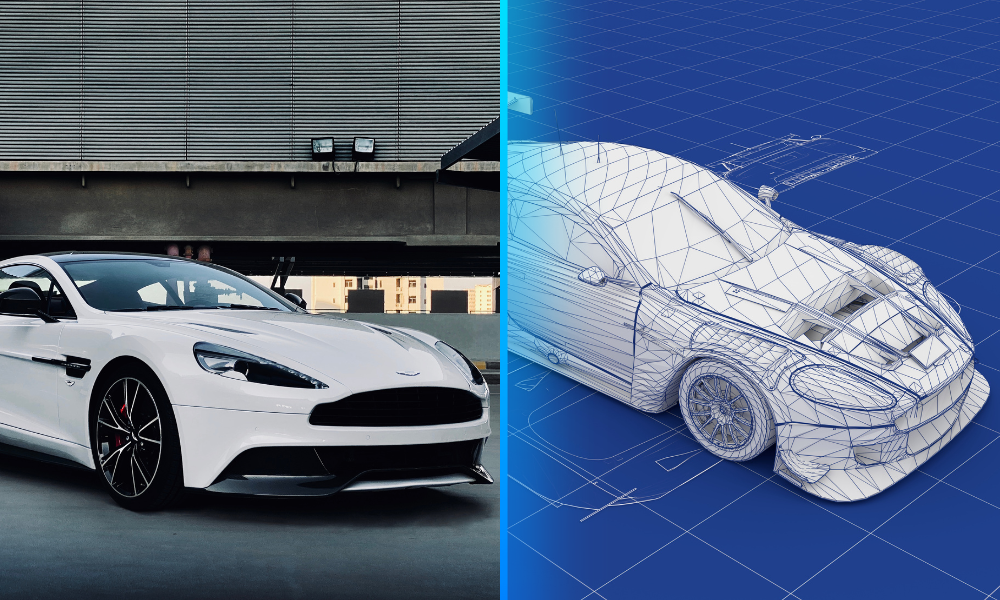
As the automotive industry undergoes a transformative shift towards sustainability, electric vehicles (EVs) have emerged as a key solution to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change. Central to the operation of electric vehicles are electric engines, which come in various types, each with its unique characteristics and applications. In this blog post, we delve into the world of electric engines, exploring their different types, key differences, and the future of electric mobility.
-
Brushed DC Motors: Brushed DC motors are among the earliest types of electric motors used in automotive applications. They rely on a system of brushes and commutators to transfer electrical power to the rotor, generating motion. While simple in design, brushed DC motors are known for their relatively low efficiency and require periodic maintenance due to brush wear.
-
Brushless DC Motors: Brushless DC motors offer several advantages over their brushed counterparts, including higher efficiency, reduced maintenance, and improved durability. These motors utilize electronic commutation instead of brushes, resulting in smoother operation and quieter performance. Brushless DC motors are widely used in modern electric vehicles for propulsion and auxiliary systems.
-
AC Induction Motors: AC induction motors, also known as asynchronous motors, are another common type of electric motor used in electric vehicles. Unlike DC motors, AC induction motors do not require brushes or commutators for operation. Instead, they rely on electromagnetic induction to produce rotational motion. AC induction motors are known for their robustness, high torque output, and suitability for high-performance applications.
-
Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSM): Permanent magnet synchronous motors employ permanent magnets in the rotor to generate magnetic fields that interact with the stator's rotating magnetic field. This synchronous operation results in efficient power conversion and precise control of motor speed and torque. PMSM motors are favored for their high power density, excellent efficiency, and responsiveness, making them ideal for electric vehicle propulsion.
-
Switched Reluctance Motors (SRM): Switched reluctance motors are a less common but emerging type of electric motor gaining attention for their unique design and potential benefits. SRM motors utilize the principle of magnetic reluctance to produce torque, with no permanent magnets in the rotor or stator. This design simplifies motor construction, reduces cost, and enhances reliability, making SRM motors suitable for certain electric vehicle applications.
Electric vehicles represent a paradigm shift in transportation, driven by advancements in electric engine technology and growing environmental consciousness. By understanding the different types of electric engines and their respective advantages, automakers can design and develop more efficient, reliable, and sustainable electric vehicles. As the electric vehicle market continues to expand, innovation in electric engine technology will play a crucial role in shaping the future of mobility towards a cleaner, greener, and more sustainable transportation system.
Powered by: Oh! Puhleeez Branding Agency & NowUpskill
Electric Vehicles, Electric Engines, Sustainable Transportation, Automotive Technology